Quick Navigation
Let’s be real – period pain can be a total nightmare. For many of us, it’s not just a minor inconvenience but a monthly battle that leaves us curled up on the couch, reaching for painkillers, and counting down the days until it’s over. But what if there was a natural way to ease the cramps, reduce the discomfort, and actually feel like yourself during your period?
Enter Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), including acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine. These ancient practices are gaining modern recognition for their ability to tackle period pain at its root, offering relief without the side effects of conventional meds.
Why Acupuncture? It’s Not Just Needles!
You might be wondering, “Does acupuncture really work for period pain?” The answer is a resounding yes! Research shows that acupuncture can be a game-changer for women dealing with dysmenorrhea (that’s the fancy term for painful periods). Here’s the scoop:
- A study published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research found that acupuncture significantly reduces period pain and is way gentler on your body compared to painkillers.
- Another review confirmed that acupuncture doesn’t just mask the pain—it helps your body heal and rebalance, so you feel better in the long run.
So, how does it work?
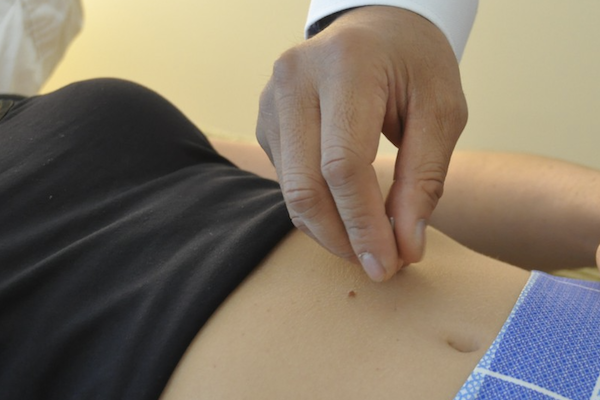
Acupuncture involves tiny, hair-thin needles placed at specific points on your body to boost blood flow, relax your uterus, and balance your energy (Qi). It’s like hitting the reset button for your body.
How TCM Tackles Period Pain
In TCM, period pain isn’t just about cramps—it’s a sign that something’s out of whack in your body. Maybe your energy is stuck, or your blood flow isn’t what it should be. A TCM practitioner will take the time to understand your unique symptoms and create a personalised plan to get you feeling your best. This might include:
1. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is all about targeting the right spots to ease your pain. Some of the go-to points for period pain include:
- Zigong (Extra Point): Near your uterus, this point helps regulate your cycle.
- Sanyinjiao (SP6): On your inner leg, it’s a powerhouse for improving blood flow and calming cramps.
- Guanyuan (CV4): On your lower abdomen, it strengthens your reproductive system.
And don’t worry—the needles are super thin, and most people find the sessions relaxing (yes, really!).
2. Chinese Herbal Medicine
Think of Chinese herbs as your period’s new best friend. They work hand-in-hand with acupuncture to soothe cramps, balance hormones, and keep your cycle running smoothly. Some popular herbs include:
- Dong Quai (Angelica sinensis): Known as the “female ginseng,” it’s a superstar for menstrual health.
- Chuan Xiong (Ligusticum wallichii): Helps get your blood moving and eases pain.
- Bupleurum (Chai Hu): Keeps your emotions in check and reduces stress-related cramps.
Popular herbal formulas for period pain include:
- Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan: Reduces cramping and promotes blood circulation.
- Xiao Yao Wan: Balances hormones and alleviates stress-related menstrual pain.
Little Changes, Big Results
While acupuncture and herbs do the heavy lifting, a few lifestyle tweaks can make a big difference too:
- Eat Warm Foods: Think soups, stews, and steamed veggies. Skip the ice-cold smoothies and salads during your period.
- Move Your Body: Gentle yoga or a walk around the block can help ease cramps and boost your mood.
- Chill Out: Stress can make period pain worse, so try meditation, deep breathing, or just curling up with a good book.
Why Choose Almond Wellness Centre?
At Almond Wellness Centre in Coburg and Ringwood, Melbourne, we’re all about helping you feel your best – naturally. Our fully qualified practitioners will:
- Take the time to understand your unique needs.
- Create a custom treatment plan just for you.
- Support you every step of the way, so you can say goodbye to period pain for good.
Ready to Ditch the Pain?
If you’re tired of letting period pain run your life, it’s time to try something different. Contact Almond Wellness Centre today to book a consultation and discover how acupuncture and Chinese medicine can help you feel your best – every day of the month.
Fill out the contact form or call our office now!
Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Xu, H., He, L., & Chen, Z. (2018). Acupuncture for primary dysmenorrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research, 44(6), 1014-1023. doi: 10.1111/jog.13631.
Armour, M. (2015). The effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea : a mixed methods study.
Mike Armour, etl July 12 2017. The role of treatment timing and mode of stimulation in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea with acupuncture: An exploratory randomised controlled trial.
V. Iorno,etl. Acupuncture Treatment of Dysmenorrhea Resistant to Conventional Medical Treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2008 Jun; 5(2): 227–230.
Acupuncture for dysmenorrhoea. Smith CA, etl.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 18;
Zhu X, Hamilton KD, McNicol ED. Acupuncture for pain in endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;5(5):CD012617. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012617.pub2.
Chiu HY, Pan CH, Shyu YK, et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome undergoing in vitro fertilisation or intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. 2020;38(1):17-28. doi: 10.1177/0964528419878323.
Smith CA, Armour M, Zhu X, Li X, Lu ZY, Song J. Acupuncture for dysmenorrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;4(4):CD007854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007854.pub3.
Lian F, Li Y, Xie RJ, Wang J, Zhang Y, Bai J. Effects of Chinese medicine for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis in treating patients with dysmenorrhea: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:8582727. doi: 10.1155/2016/8582727.
Shi GX, Yang XM, Liu CZ, et al. Acupuncture for chronic low back pain: a multicenter, randomized, patient-assessor blind, sham-controlled clinical trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(8):592-601. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002885.